The sacrum is at the base of your spine. It’s key for supporting your body and helping you move. This article will explore the sacrum’s anatomy, its role, and why it matters for your health. Knowing about the sacrum can help you take better care of your lower back and improve your life.
Key Takeaways
- The sacrum is a triangular-shaped bone that forms the foundation of the spine, connecting it to the pelvis.
- The sacral vertebrae, sacral hiatus, and sacral foramina are essential anatomical features that play crucial roles in nerve and spinal cord protection.
- The sacroiliac joint, a vital connection between the sacrum and the iliac bones, facilitates movement and stability in the pelvis.
- Sacral promontory, a bony landmark, and the sacral curvature, a spinal curve, contribute to the overall structure and function of the lower spine.
- Sacral nerves, originating from the sacral canal, provide innervation to the lower body, making them crucial for various bodily functions.
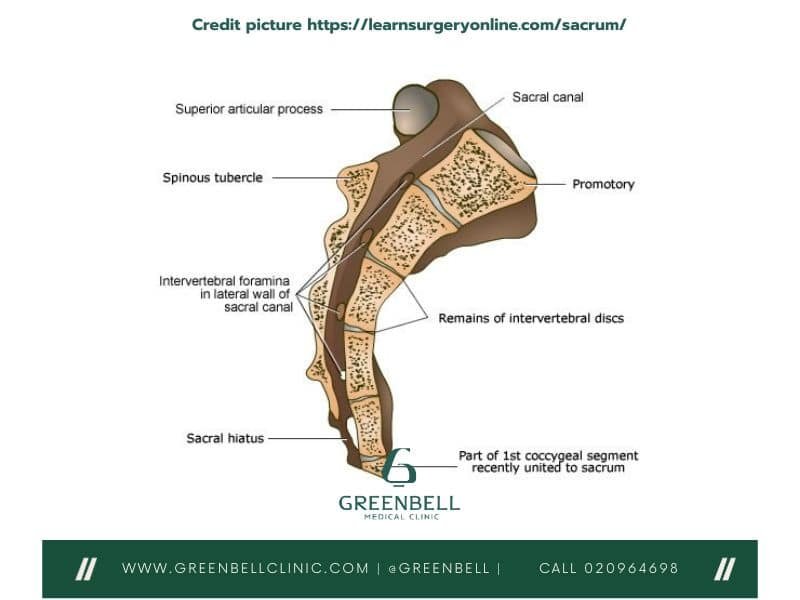
What is the Sacrum?
The sacrum is a key part of our skeletal system. It’s a triangular bone at the spine’s base. It helps move weight from the upper body to the legs. It’s made of five fused vertebrae, giving it a special shape and function.
Location and Structure
The sacrum sits between the hip bones. It’s shaped like a triangle and has special vertebrae. These features help it move smoothly and carry weight well.
Its sacral curvature is important for the spine’s shape. It keeps the body aligned right. This shape, along with the sacral vertebrae, is crucial for the body’s mechanics.
“The sacrum is a crucial component of the human skeletal system, serving as a bridge between the spine and the lower body.”
Knowing about the sacrum helps us understand our body’s mechanics. It shows how important this bone is for our movement and health.
Sacral Vertebrae: The Building Blocks
The sacral vertebrae are at the heart of the sacrum. They are five fused vertebrae that form the base of the lower spine. These vertebrae, labeled S1 to S5, are designed to provide strong support to the entire skeletal system.
The sacral promontory is a key feature of the sacral vertebrae. It is the top part of the sacrum and is important for medical procedures. The sacral foramina are also crucial. They are openings through which nerves and blood vessels pass, connecting the sacrum to the rest of the body.
The sacral vertebrae are vital for keeping the spine curved. This curve, known as the sacral curve, adds stability to the body. It also helps in absorbing shock and distributing weight evenly, ensuring good function and mobility.
- The five sacral vertebrae (S1 to S5) are fused together, creating a strong and stable foundation for the spine.
- The sacral promontory serves as an important anatomical landmark, particularly in medical procedures.
- The sacral foramina allow for the passage of nerves and blood vessels, connecting the sacrum to the rest of the body.
- The sacral curve, formed by the sacral vertebrae, helps to maintain spinal alignment and distribute weight evenly.
Understanding the anatomy of the sacral vertebrae is key to a healthy spine. These building blocks of the lower back are vital for our overall musculoskeletal health.
Sacral Hiatus and Foramina
The human body is amazing, with every part playing a key role. The sacrum, a part of the lower spine, is one such important element. It has two main features: the sacral hiatus and the sacral foramina. These parts are vital and help us understand our bodies better.
The Sacral Hiatus: A Unique Opening
The sacral hiatus is a special opening at the bottom of the sacrum. It lets the sacral canal pass through, carrying the spinal cord and nerves to the lower body. This opening is key for sending and receiving messages from the lower body.
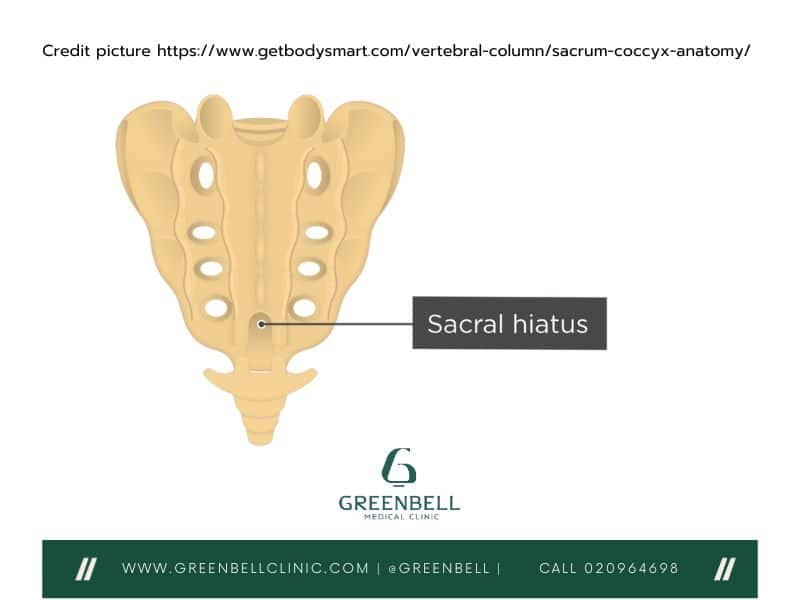
Sacral Foramina: Pathways for Nerves and Blood Vessels
The sacrum also has sacral foramina, which let nerves and blood vessels through. These openings are along the sacrum, helping to spread out important neural and vascular elements to nearby tissues and organs.
The sacral canal, made by the sacral vertebrae, is also vital. It protects the spinal cord and its branches, ensuring they travel safely.
| Feature | Function | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Sacral Hiatus | Provides a pathway for the spinal cord and nerves to extend into the lower body | Facilitates the transmission of sensory and motor information to and from the lower extremities |
| Sacral Foramina | Allow nerves and blood vessels to pass through the sacrum | Enables the distribution of neural and vascular components to surrounding tissues and organs |
| Sacral Canal | Protects the spinal cord and its branches as they pass through the sacrum | Ensures the safe passage of these vital neural structures |
Learning about the sacrum’s details, like the sacral hiatus, sacral foramina, and sacral canal, helps us appreciate the human body’s design. It shows how each part is crucial for our health and well-being.
Sacral Canal: The Nerve Pathway
The sacral canal is a special part of the sacrum, located in the middle. It’s a key part of the spinal canal. Inside, the sacral nerves live. These nerves help control the lower body, like the legs, feet, and muscles in the pelvis.
The sacral canal is vital for nerve health and the well-being of the lower body. It lets the sacral nerves travel through the sacrum. This is how they send important messages to different parts of the body. If the sacral canal gets damaged, it can cause serious health problems.
| Sacral Canal Features | Importance |
|---|---|
| Continuation of the spinal canal | Provides a protected passageway for the sacral nerves |
| Houses the sacral nerves | Enables the transmission of sensory and motor signals to the lower body |
| Integrity of the canal | Crucial for maintaining proper nerve function and lower body health |
Knowing about the sacral canal is important for doctors and everyone else. It helps us understand how the lower body works. This knowledge helps us find better ways to deal with health issues related to the sacral canal.
Sacroiliac Joint: The Crucial Connection
The sacroiliac joint connects the sacrum to the two iliac bones. It’s key for the body’s movement and stability. This joint transfers forces from the top to the bottom of the body.
Anatomy and Biomechanics
The sacroiliac joint is made to handle a lot of stress. It’s a complex joint that is both stable and mobile. This makes it essential for our daily activities.
The sacral curvature and sacral promontory are important for the joint’s function. They help spread out weight and forces. This makes the joint more stable and able to handle more weight.
The joint’s biomechanics also depend on the ligaments and muscles around it. These help support the joint, limit too much movement, and help move forces smoothly.
“The sacroiliac joint is truly the unsung hero of the musculoskeletal system, quietly yet profoundly impacting our daily lives through its crucial role in movement and stability.”
Knowing about the sacroiliac joint and its role is key for spinal and pelvic health. It helps us understand how our body works and moves.
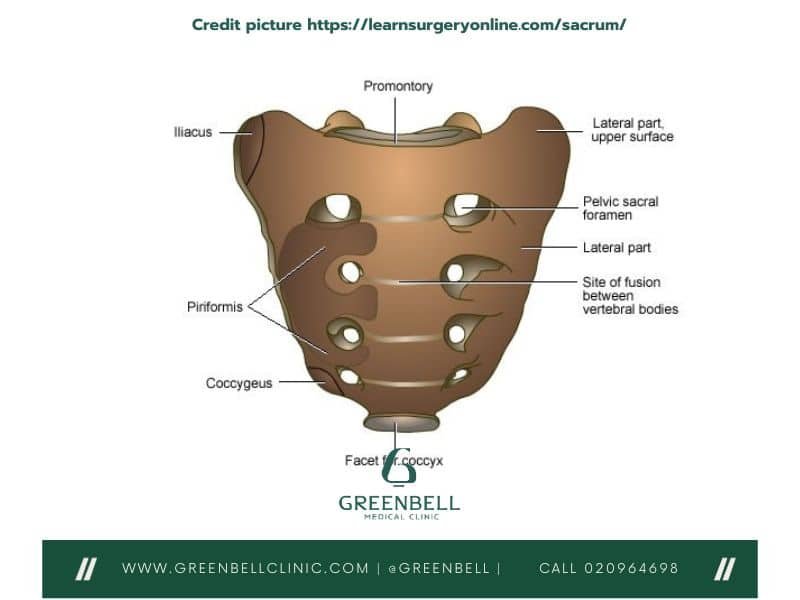
Sacrum Anatomy
The sacrum is a unique bone in the lower spine and pelvis. It’s shaped like a triangle and made of five fused vertebrae. This shows how cleverly the human body is designed.
The sacral vertebrae are at the heart of the sacrum. Each vertebra has its own role and features. They work together with other parts to support the spine and pelvis. The sacroiliac joint connects the sacrum to the pelvis. It helps with both stability and movement.
Looking into the sacrum’s anatomy, we find many interesting details. There’s the sacral hiatus at the spine’s base and many foramina for nerves and blood vessels. Every part of the sacrum is important for the body’s function.
| Anatomical Feature | Function |
|---|---|
| Sacral Vertebrae | Provide structural support and stability to the lower spine and pelvis. |
| Sacroiliac Joint | Facilitates movement and weight-bearing between the sacrum and the pelvis. |
| Sacral Hiatus | Allows the passage of nerves and blood vessels, and serves as an important landmark for medical procedures. |
| Sacral Foramina | Enable the exit of spinal nerves, contributing to the nervous system’s function. |
Understanding the sacrum’s anatomy helps us appreciate the body’s design. It shows how important this bone is for our health.
Sacral Promontory: The Bony Landmark
The sacral promontory is a key part of our body. It’s important for the lower spine’s structure and function. This bony landmark is at the top, front part of the sacrum. It marks where the lumbar spine meets the pelvis.
The sacral promontory affects the sacroiliac joint and sacral curvature. It shapes the sacrum, which is crucial for the joint’s connection to the pelvis. This joint is between the sacrum and the iliac bones.
- The sacral promontory is a key reference for checking the sacroiliac joint’s alignment and stability.
- Any issues with the sacral promontory can lead to spinal and pelvic problems. This includes low back pain and sacroiliac joint dysfunction.
The sacral promontory also impacts the sacrum’s curvature. This curvature is part of the spine’s natural S-shape. It helps spread weight and stress in the lower back and pelvis. This is important for good posture and movement.
“Understanding the anatomical features of the sacral promontory is crucial for healthcare professionals when evaluating and treating patients with lower back, pelvic, or hip-related conditions.”
In summary, the sacral promontory is vital for the lower spine and pelvis. Its location and effects on the sacroiliac joint and sacral curvature are key. It’s important for diagnosing and treating many musculoskeletal issues.
Sacral Curvature: The Spinal Curve
The human spine is a wonder of nature. Each part is vital for our posture and movement. The sacrum, a triangular bone, is at the spine’s base. It forms the pelvis’s keystone.
The sacrum has a natural curve, called the sacral curvature. This curve continues from the lumbar lordosis, the inward curve of the lower back.
Importance and Implications
The sacral curvature is key to our spinal alignment. It helps distribute weight and ensures our biomechanics work well. This curve works with the sacroiliac joint and the sacral promontory to help us move smoothly.
This curvature keeps the spine’s natural S-shape. It’s vital for shock absorption, reducing stress on the vertebrae, and promoting good posture. If the sacral curvature is off, we might face lower back pain, balance problems, and less mobility.
- The sacral curvature is a continuation of the lumbar lordosis, forming the natural S-shaped curve of the spine.
- This curvature is essential for weight distribution, shock absorption, and overall spinal alignment.
- The sacral curvature works in tandem with the sacroiliac joint and sacral promontory to facilitate efficient movement.
- Alterations in the sacral curvature can contribute to various musculoskeletal problems, emphasizing the importance of maintaining a healthy spinal alignment.
Understanding the sacral curvature and its role in the spine is key. It helps keep our lower back healthy and pain-free. By knowing how the sacrum supports our spine, we can better care for this important area.
Sacral Nerves: The Nervous System Connection
The sacral nerves are found in the sacrum. They play a key role in our body’s nervous system. These nerves help control the lower body, including the legs, feet, and pelvic muscles.
These nerves are part of the lumbosacral plexus. This network helps with movement and feeling in the lower body. They pass through the sacral foramina, tiny openings in the sacrum. This lets them send important messages to the brain.
| Sacral Nerve Functions | Anatomical Locations |
|---|---|
| Sensory innervation of the skin and muscles in the lower body | Originate from the sacral canal and pass through the sacral foramina |
| Motor control of the pelvic floor muscles, bladder, and rectum | Part of the lumbosacral plexus, a complex network of nerves |
| Coordination of bowel, bladder, and sexual function | Responsible for innervating the legs, feet, and pelvic region |
The sacral nerves are vital for our lower body’s health. Problems with these nerves can cause pain, incontinence, and sexual issues. Knowing about the sacral nerves helps doctors and patients keep the lower body healthy.
Sacral Fractures and Disorders
The sacrum is a key part of the lower spine. It can get injured or develop disorders. These issues can lead to pain, instability, and problems with the lower body. It’s important to know about the causes, symptoms, and treatments to get the right care.
Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Sacral fractures can happen from accidents or falls, or from conditions like osteoporosis. Symptoms include severe back pain, trouble walking, and sacral nerve damage. Treatment may include pain relief, rest, and sometimes surgery.
Sacroiliac joint dysfunction affects the joint between the sacrum and pelvis. It can cause pain, limited movement, and pain in the hips or legs. First, doctors might try physical therapy, medicine, or injections to help.
Other sacral disorders like sacral nerve damage and tumors or cysts can also affect health. These need special tests and treatment plans to fix the problem and ease symptoms.
Getting medical help quickly and using a detailed approach is key. It helps restore function, reduce pain, and avoid long-term problems. Working with doctors is important to find the best way to recover.
The Sacrum’s Role in Daily Life
The sacrum is a key part of our skeleton. It helps us stand, walk, and balance. This triangular bone at the spine’s base transfers weight from the top to the bottom of our body.
The sacrum works with the sacroiliac joint and the pelvis. Together, they make our movements smooth. The sacral nerves in the sacral canal are also important. They help with feeling and movement in our legs.
Problems like fractures or degeneration in the sacrum can affect our daily activities. It’s important to fix these issues to keep our health and quality of life good. The sacrum’s role is vital for our physical health.
“The sacrum is the unsung hero of the human body, quietly supporting us through the ups and downs of daily life.”
Knowing how important the sacrum is helps us take care of it. This way, our bodies stay strong and ready for our daily tasks.
Conclusion: Understanding the Sacrum’s Significance
The sacrum is a remarkable structure, serving as the foundation of the spine. It plays a vital role in supporting the body’s movements. By exploring the sacrum anatomy, the intricate network of sacral vertebrae, and the crucial sacroiliac joint, we’ve gained a deeper appreciation for this often overlooked part of the human frame.
The sacral nerves that originate from the sacrum connect the lower back to the rest of the body. This allows for seamless coordination and function. Understanding the potential sacral disorders and how to address them is equally important. It empowers us to maintain a healthy and active lifestyle.
Ultimately, the sacrum’s significance extends far beyond its physical structure. It is a testament to the body’s remarkable adaptability and the interplay between its various systems. By staying informed and proactive about the sacrum’s role, we can unlock the key to better posture, mobility, and overall well-being.





