Did you know that osteoarthritis of the knee affects millions of people worldwide and its prevalence increases with age? This osteoarthritis can cause pain, stiffness, and loss of mobility, affecting daily life and overall health. However, the key to effectively managing osteoarthritis of the knee lies in finding the early indicators and getting the right treatment. This article explores the importance of recognizing the early signs of knee osteoarthritis and how they can lead to long-term outcomes.
Key Takeaways:
- Spotting the early indicators of knee osteoarthritis is crucial for timely intervention and effective management.
- Persistent knee pain, joint stiffness, and audible sounds from the knee are potential early signs of knee osteoarthritis.
- Understanding the impact of cartilage on knee joint health and the role of risk factors can help assess the likelihood of developing knee osteoarthritis.
- Consulting a specialist and undergoing diagnostic approaches are essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
- Effective knee osteoarthritis management involves a holistic approach, including medication, physical therapy, weight management, and lifestyle changes.
Understanding Knee Osteoarthritis and Its Impact
Osteoarthritisof the knee, also known as knee OA, is a degenerative joint disease that affects the kneejoint. It is characterized by the gradualdestructionand loss of cartilage,causingpain, stiffness, inflammation, andlossofmobility. Early detection ofosteoarthritis of thekneeiscriticaltopreventfurtherjointdamage and allowtimely intervention and management toimprove quality of life. Cartilage playsanimportantrole in knee joint healthbecauseit acts as a cushion betweenbones, absorbing shock andallowingsmoothmovementofthejoint. Ascartilage deteriorates or wears away, the bonesrubagainst each other, causingknee jointpain and other symptoms associated withOA.
To understand the impact of osteoarthritis of the knee, it is important to recognize the importance of early detection and the role of cartilage in knee joint health. By staying informed about the causes, symptoms, and treatments of knee osteoarthritis, you can take proactive steps to effectively manage your condition and improve your overall quality of life.
Risk Factors Associated with Knee Osteoarthritis
Several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing knee osteoarthritis. These factors include:
- Age (especially above 50 years old)
- Gender (women are more prone to knee OA)
- Previous knee injury or surgery
- Obesity or excessive weight
- Repetitive stress on the knee joints (e.g., due to certain occupations or sports activities)
- Genetic predisposition
- Underlying medical conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or gout
Understanding these risk factors can help individuals assess their own risk and take preventive measures to reduce the chances of developing knee osteoarthritis.
Indicator for Knee Osteoarthritis: Recognizing the Early Signs
Recognizing the early signs of knee osteoarthritis is crucial for timely intervention and effective management. Recognizing these signs will allow you to seek professional help for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Below are three early signs to watch for:
The Significance of Persistent Knee Pain
Persistent knee pain that lasts longer than 6 months, especially during activities such as walking, climbing stairs, or sitting for long periods of time, is an important indicator of osteoarthritis of the knee. If knee pain persists, it is important to consult a health care professional for a detailed examination.
Joint Stiffness and Loss of Flexibility
Knee osteoarthritis can also manifest as joint stiffness and a gradual loss of flexibility, especially after periods of inactivity. If you notice difficulty in bending or straightening your knee, or if your knee feels stiff and takes time to loosen up, it may be an early sign of knee osteoarthritis.
Audible Sounds from the Knee as an Indicator
Another indicator of knee osteoarthritis is the presence of audible sounds, such as cracking, popping, or grinding, when moving the knee joint. These sounds, known as crepitus, can occur during bending, squatting, or other knee movements. If you consistently experience these sounds, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
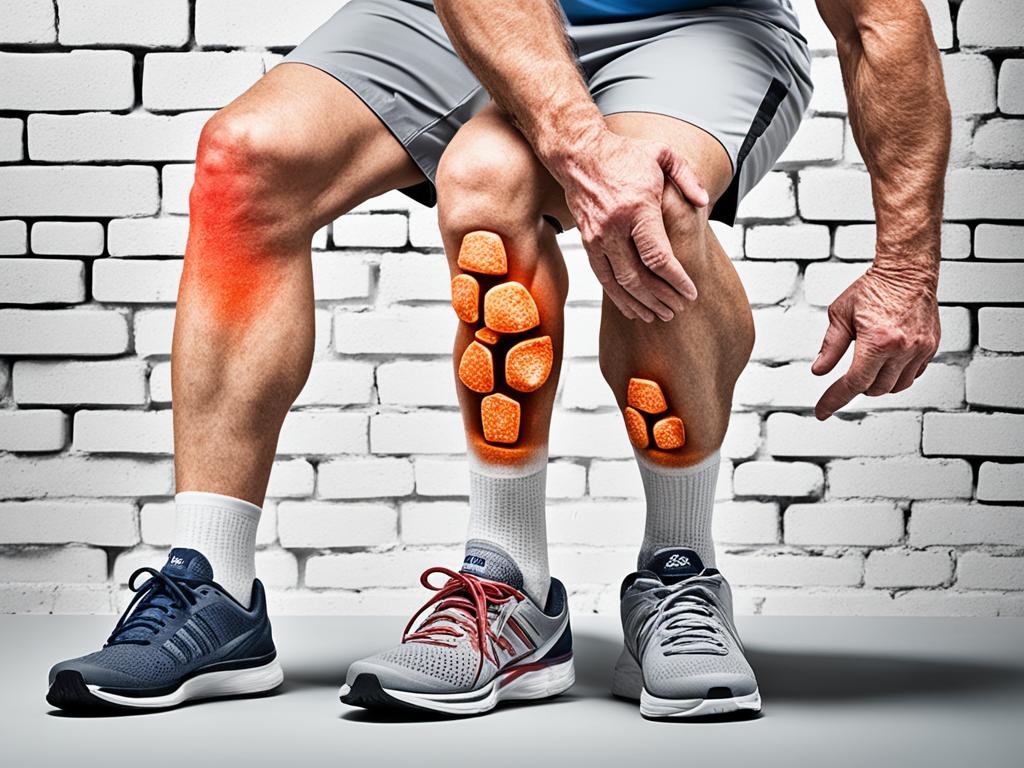

Knee Osteoarthritis Symptoms: More Than Just Pain
Knee osteoarthritis is often associated with pain, but it can also present with other symptoms. These symptoms may include swelling, tenderness, warmth or redness in the affected knee, limited range of motion, muscle weakness, instability or buckling of the knee, and changes in the appearance or shape of the joint. It is important to recognize these symptoms and seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and management.
Common Misconceptions About Knee Osteoarthritis Symptoms
There are several common misconceptions about knee osteoarthritis (OA) symptoms that need to be clarified. It is crucial to dispel these misconceptions in order to ensure individuals have accurate information about their condition and can make well-informed decisions about their treatment. In this section, we will address two common misconceptions associated with knee OA: distinguishing OA from other joint issues and the myth of inevitable pain progression in knee OA.
Distinguishing OA from Other Joint Issues
Distinguishing knee OA from other joint issues can be challenging, as symptoms may overlap with conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or tendonitis. It is important to consult a specialist for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Seeking medical advice from a healthcare professional who specializes in musculoskeletal conditions will help differentiate knee OA from other joint issues and ensure that you receive the most effective treatment for your specific condition.
The Myth of Inevitable Pain Progression in Knee OA
Another common misconception about knee OA is the belief that pain progresses and inevitably worsens over time. While it is true that knee OA is a progressive disease, with proper management and lifestyle modifications, pain can be effectively managed and functional mobility maintained. A combination of medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications can help maintain quality of life and prevent unnecessary pain and disability caused by knee OA. It is important to work closely with your health care professional to develop an individualized treatment plan that addresses your unique needs and goals.
| Common Misconceptions About Knee OA Symptoms | Reality |
|---|---|
| Distinguishing OA from other joint issues is easy | Distinguishing OA from other joint issues can be challenging, and it requires a specialist’s expertise for accurate diagnosis and treatment. |
| Pain in knee OA will inevitably progress and worsen over time | With proper management and lifestyle modifications, individuals with knee OA can effectively manage pain and maintain functional mobility. |
Consulting a Specialist: When to Seek Professional Help
If you suspect or experience any symptoms of knee osteoarthritis, it is important to consult a specialist for a proper evaluation and diagnosis. A specialist, such as an orthopedic doctor or rheumatologist, will have the expertise to assess your symptoms, conduct diagnostic tests, and recommend appropriate treatment options. Seeking professional help early on can lead to better outcomes and improved quality of life.
Diagnostic Approaches to Confirming Knee Osteoarthritis
Confirming a diagnosis of knee osteoarthritis requires various diagnostic approaches. These approaches include non-invasive techniques and imagery, as well as physical exams and patient history assessments. By combining these diagnostic approaches, healthcare professionals can accurately confirm knee osteoarthritis and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Non-Invasive Techniques and Imagery
Non-invasive techniques, such as X-rays or MRI scans, play a crucial role in confirming knee osteoarthritis. These imaging techniques provide detailed visuals of the knee joint, allowing healthcare professionals to assess the extent of cartilage damage and other joint abnormalities. By examining the images, doctors can make an accurate diagnosis and determine the severity of the condition.
Understanding the Role of Physical Exams and Patient History
In addition to imaging techniques, physical exams and patient history assessments are important diagnostic tools for knee osteoarthritis. During a physical exam, healthcare professionals assess the patient’s symptoms, joint mobility, and overall knee function. This examination helps identify specific signs of knee osteoarthritis, such as swelling, tenderness, and reduced range of motion.
Furthermore, patient history assessments provide valuable information about the individual’s medical background, including previous knee injuries or surgeries, underlying medical conditions, and family history of arthritis or joint diseases. The information gathered from patient history helps doctors understand the context of the knee osteoarthritis and make an accurate diagnosis.
By combining non-invasive techniques, physical exams, and patient history assessments, healthcare professionals can confirm the presence of knee osteoarthritis and create a tailored treatment plan to address the individual’s specific needs.
Knee Osteoarthritis Treatment Options for Relief and Management
When it comes to treating knee osteoarthritis, there are several options available that can provide both relief and effective management of the condition. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the condition and the individual’s specific needs, so it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate approach.
One of the common treatment options for knee osteoarthritis is medication. Medications can help manage pain and inflammation, reducing discomfort and improving daily functioning. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and analgesics are commonly prescribed to control symptoms.
In addition to medication, physical therapy is another valuable treatment option. Physical therapy can help improve joint mobility, strengthen the muscles around the knee joint, and enhance overall functional ability. A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program tailored to the individual’s needs and goals.
Assistive devices such as braces or crutches can also provide support and stability for individuals with knee osteoarthritis. These devices help distribute weight and reduce pressure on the affected knee joint, alleviating pain and enhancing mobility.
In some cases, injections may be recommended to reduce pain and inflammation. Corticosteroid injections or hyaluronic acid injections can provide temporary relief and improve joint function.
If knee osteoarthritis is severe and conservative treatments do not provide sufficient relief, surgical interventions may be considered. Arthroscopy or joint replacement surgery are options for individuals with advanced knee osteoarthritis to alleviate pain and improve joint function.
Overall, the treatment options for knee osteoarthritis aim to provide relief from pain and discomfort, improve joint mobility, and enhance the individual’s overall quality of life. Consulting with a healthcare professional is key to determining the most suitable treatment approach based on the individual’s specific needs and preferences. With the right treatment, individuals can effectively manage knee osteoarthritis and find relief from their symptoms.
Knee Osteoarthritis Management: Beyond Medication
Managing knee osteoarthritis involves more than just medication. Physical therapy and exercise play a crucial role in improving joint mobility, reducing pain, and strengthening the muscles around the knee joint. Physical therapists can design personalized exercise programs to suit individual needs and help manage knee osteoarthritis effectively. Additionally, weight management is essential for reducing the burden on the knee joints. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular physical activity can significantly alleviate knee OA symptoms and improve overall joint health.
Preventing Knee Osteoarthritis: Lifestyle Changes and Intervention Strategies
Preventing knee osteoarthritis involves making lifestyle changes and adopting intervention strategies. By incorporating a knee-friendly diet and engaging in low-impact exercises, individuals can reduce the risk of developing knee osteoarthritis and promote long-term joint health.
Incorporating a Knee-Friendly Diet
One effective way to prevent knee osteoarthritis is by incorporating a knee-friendly diet. Consuming foods that are rich in nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants can help reduce inflammation and support joint health. Foods such as fatty fish, nuts, seeds, and colorful fruits and vegetables are great additions to a knee-friendly diet. These nutrients have been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties that can benefit the joints and help prevent knee osteoarthritis.
Engaging in Low-Impact Exercises for Joint Health
Engaging in low-impact exercises is another key strategy for preventing knee osteoarthritis. Low-impact exercises help strengthen the muscles around the knee joint without exerting excessive pressure on the joints. Activities such as swimming, cycling, and walking are excellent options. These exercises improve joint stability, flexibility, and overall joint health, reducing the risk of developing knee osteoarthritis. Regular physical activity also helps maintain a healthy weight, which further reduces the strain on the knee joints.
Incorporating a knee-friendly diet and engaging in low-impact exercises are proactive measures individuals can take to prevent knee osteoarthritis. By making these lifestyle changes, individuals can reduce the risk of developing this condition and maintain long-term joint health.
The Advancements in Knee Osteoarthritis Care and Technologies
Advances in knee osteoarthritis (OA) care and technologies have revolutionized the management and treatment options for individuals with this condition. These advancements encompass innovative surgical techniques, such as minimally invasive procedures and robot-assisted surgery, as well as the development of new medications and therapies.
One noteworthy technology-based intervention is TECAR technology, offered at Greenbell Clinic. This cutting-edge treatment has shown promising results in accelerating bone regeneration and providing relief for knee OA. By utilizing TECAR technology, patients can experience improved joint health and a reduction in pain, allowing them to lead a more active and fulfilling life.
Staying informed about these advancements is vital for individuals with knee OA, as it empowers them to make informed decisions about their treatment options. Through continuous research and innovation, the field of knee OA care continues to evolve, offering new possibilities for improved outcomes and enhanced quality of life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, knee osteoarthritis is a common condition that can cause pain and discomfort. However, by adopting a holistic approach to knee OA management, individuals can minimize its impact on their daily lives. This approach involves making lifestyle changes, such as incorporating a knee-friendly diet, engaging in low-impact exercises, and maintaining a healthy weight through regular physical activity. Additionally, physical therapy and medication can help alleviate pain and improve joint mobility.
Spotting early indicators of knee osteoarthritis is crucial for better long-term outcomes. By recognizing persistent knee pain, joint stiffness, loss of flexibility, and audible sounds from the knee joint, individuals can seek professional help for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Furthermore, education and awareness play a critical role in preventing knee osteoarthritis. By educating individuals about the risk factors associated with knee OA and promoting awareness of preventive measures, such as maintaining a healthy lifestyle and avoiding repetitive stress on the knee joints, the prevalence of this condition can be reduced. Taking proactive steps and seeking professional help are key in effectively managing knee osteoarthritis and leading a healthier, more active life.
FAQ
What are the indicators of knee osteoarthritis?
The indicators of knee osteoarthritis include persistent knee pain, joint stiffness and loss of flexibility, and audible sounds from the knee joint.
Why is early detection of knee osteoarthritis important?
Early detection of knee osteoarthritis allows for timely intervention and management to prevent further joint damage and improve quality of life.
What is the role of cartilage in knee joint health?
Cartilage acts as a cushion between the bones in the knee joint, absorbing shock and enabling smooth joint movement.
What are the risk factors associated with knee osteoarthritis?
Risk factors for knee osteoarthritis include age (especially above 50 years old), gender (women are more prone), previous knee injury or surgery, obesity, repetitive stress on the knee joints, genetic predisposition, and underlying medical conditions.
What are the early signs of knee osteoarthritis?
The early signs of knee osteoarthritis include persistent knee pain, joint stiffness and loss of flexibility, and audible sounds from the knee joint.
What are the symptoms of knee osteoarthritis?
Symptoms of knee osteoarthritis may include pain, swelling, tenderness, reduced range of motion, muscle weakness, instability or buckling of the knee, and changes in the appearance or shape of the joint.
Are there any misconceptions about knee osteoarthritis symptoms?
Yes, there are misconceptions about knee osteoarthritis symptoms, including the difficulty of distinguishing it from other joint issues and the belief that pain will inevitably progress and worsen over time.
When should I consult a specialist for knee osteoarthritis?
You should consult a specialist, such as an orthopedic doctor or rheumatologist, if you suspect or experience any symptoms of knee osteoarthritis for a proper evaluation and diagnosis.
How is knee osteoarthritis diagnosed?
Knee osteoarthritis can be diagnosed through non-invasive techniques such as X-rays or MRI scans, as well as physical exams and patient history.
What are the treatment options for knee osteoarthritis?
Treatment options for knee osteoarthritis may include medication, physical therapy, assistive devices, injections, and in severe cases, surgical interventions.
How can I manage knee osteoarthritis beyond medication?
Managing knee osteoarthritis involves physical therapy and exercise to improve joint mobility and strength, as well as weight management to reduce the burden on the knee joints.
How can I prevent knee osteoarthritis?
Preventing knee osteoarthritis involves making lifestyle changes, incorporating a knee-friendly diet, and engaging in low-impact exercises for joint health.
What are the advancements in knee osteoarthritis care and technologies?
Advancements in knee osteoarthritis care and technologies include innovative surgical techniques, new medications and therapies, and technology-based interventions like TECAR technology.
What is the importance of adopting a holistic approach to knee osteoarthritis management?
Adopting a holistic approach to knee osteoarthritis management involves addressing multiple aspects of the condition, such as medication, physical therapy, exercise, and weight management, to improve symptoms and overall joint health.

